

Generating high volumes of professional, customized documents can be challenging, especially when relying on manual processes.
Python, known for its automation capabilities and extensive libraries, simplifies workflows but often needs a specialized solution to handle template design, data integration, and large-scale distribution.
This is the time that EDocGen comes in, pairing perfectly with Python to automate document generation easily.
Designed to work smoothly with Python, EDocGen helps:
So, if your concerns revolve around simplifying PDF generation in Python, this guide will show you how eDocGen can make it faster and more efficient.
Getting started with EDocGen is simple and straightforward, even for those new to document automation. With just a few quick steps, you can begin creating professional PDF documents using Python.
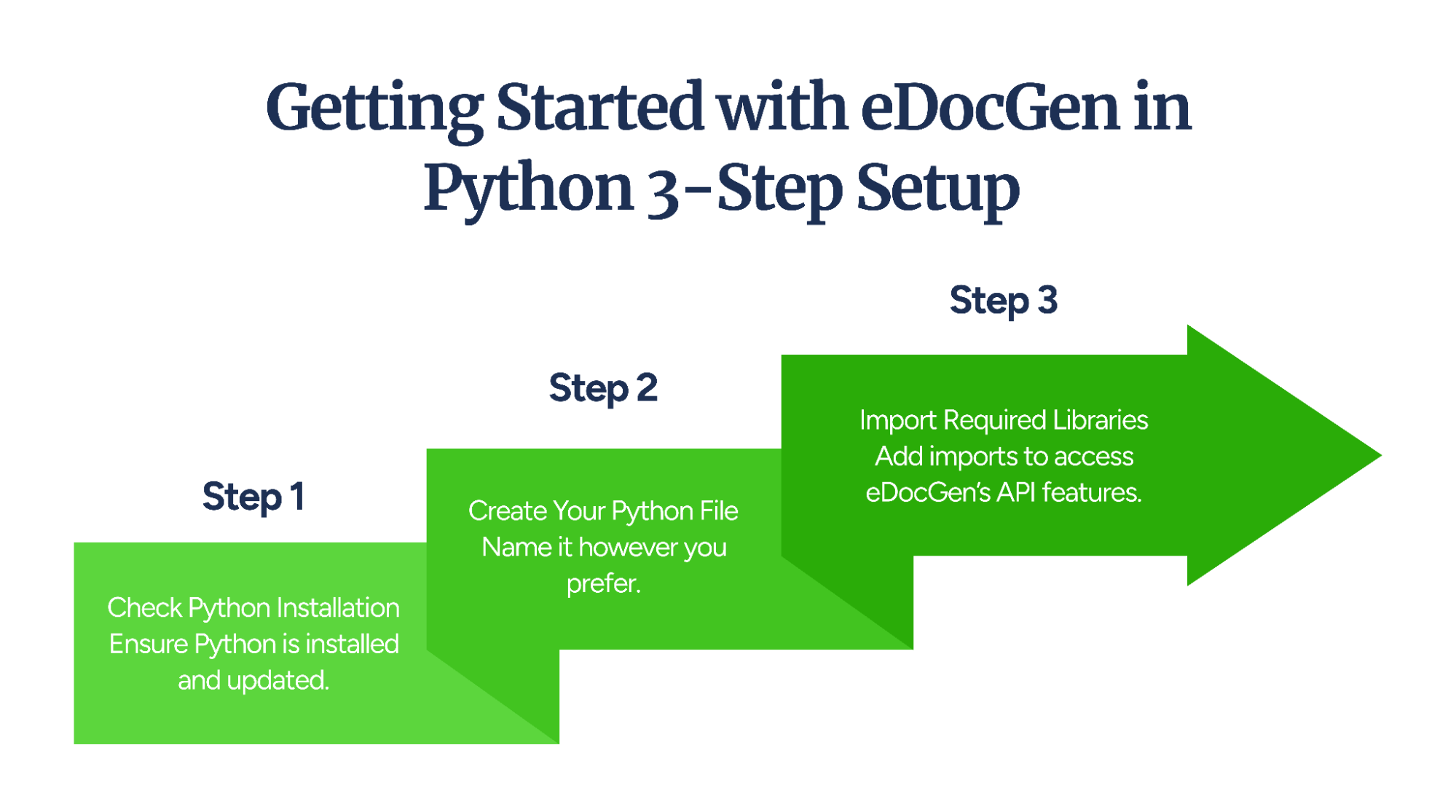
First, ensure that Python is installed and updated on your system.
To check your Python version, run the command below in your terminal or command prompt:
``` python --version ```
If the version displayed isn’t the latest, consider updating Python to avoid any compatibility issues and ensure smooth operation with EDocGen.
Next, create a new Python file.
You can name it "eDocGenapi.py" or choose any name that suits your project. This file will serve as the foundation for integrating EDocGen with Python.
To access eDocGen's API features, include the following import statements at the top of your Python file:
```
from email import header
import requests
import uuid
import os.path
import json
```
These libraries enable your Python script to communicate with EDocGen's platform, manage API requests, and handle data inputs efficiently.
The setup is straightforward and efficient, helping you start the document automation process faster than you might expect.
Once this foundation is ready, the next step focuses on automating document generation using Python and EDocGen.
As we learned above, automating document generation doesn’t have to be complex.
With just a few lines of code, EDocGen simplifies PDF creation in Python, whether it’s on-demand, bulk generation, or database-driven automation.
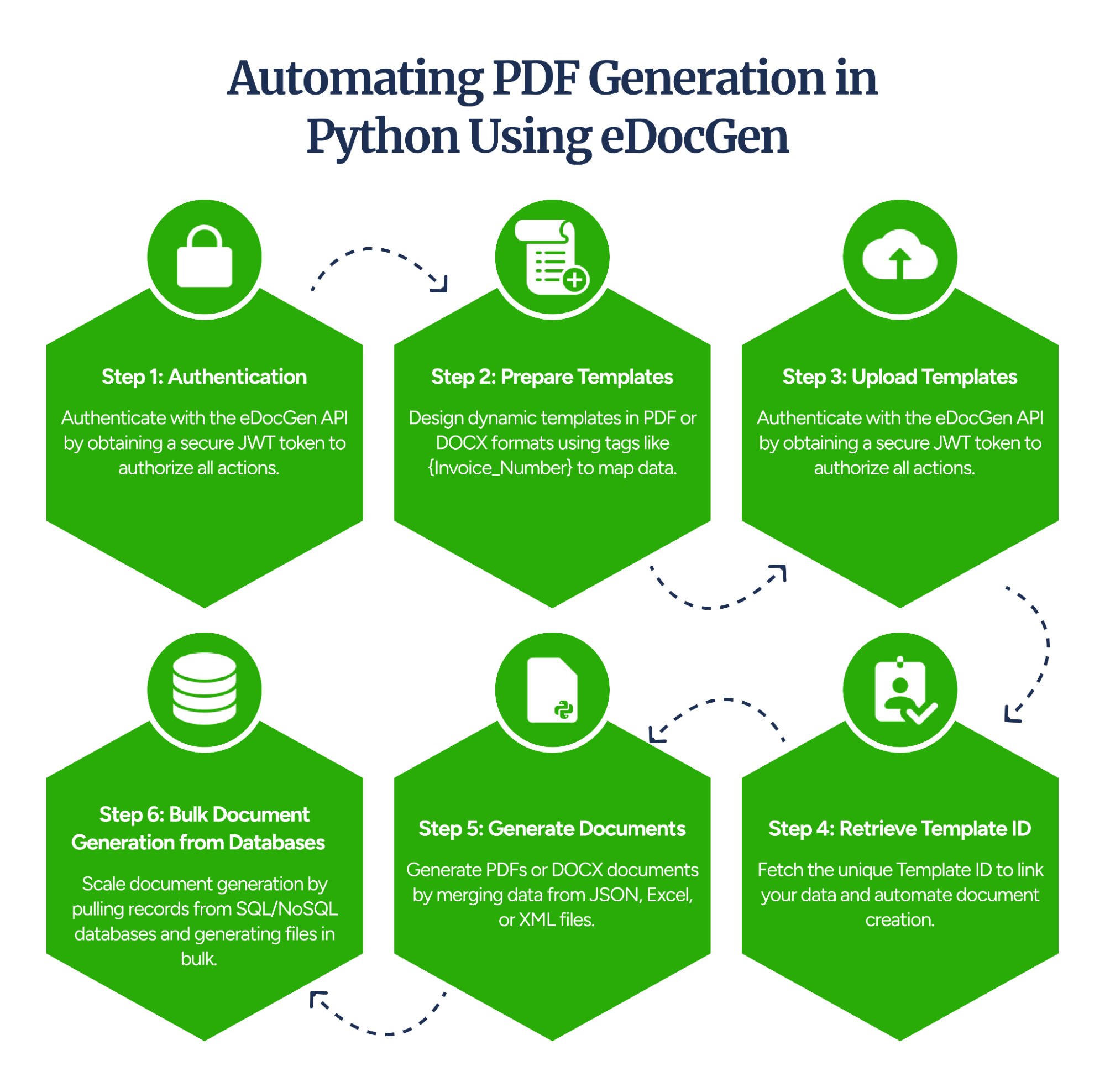
Here’s how to execute automate document generation using Python and EDocGen:
To interact with EDocGen’s API, you’ll first need to authenticate using a JWT-based token.
For getting started, you need to register and obtain an access token by passing your username and password to the /login endpoint. This token is required for every subsequent API call to authorize your actions.
We will create an init method in the Python code to fetch and store the token for later use:
```
class eDocGenapi:
token = ""
def init(self):
base_url = "https://app.edocgen.com"
url = "%s/login" % base_url
payload = "{\n\t\"username\":\"\",\n\t\"password\": \"\"\n}"
headers = {
'content-type': "application/json",
'cache-control': "no-cache",
}
response = requests.request("POST", url, data=payload, headers=headers)
x_access_token = response.json()['token']
eDocGenapi.token = x_access_token
print(x_access_token)
```
eDocGen enables users to customize and upload their templates, so before generating documents, create a dynamic template in PDF or Microsoft Word format.
Use curly braces {} to define dynamic fields, known as tags, which will be replaced with actual data during generation.
Example Tags:
Dynamic tables can also be created using {#tablename} and {/tablename} to automatically populate rows with data.
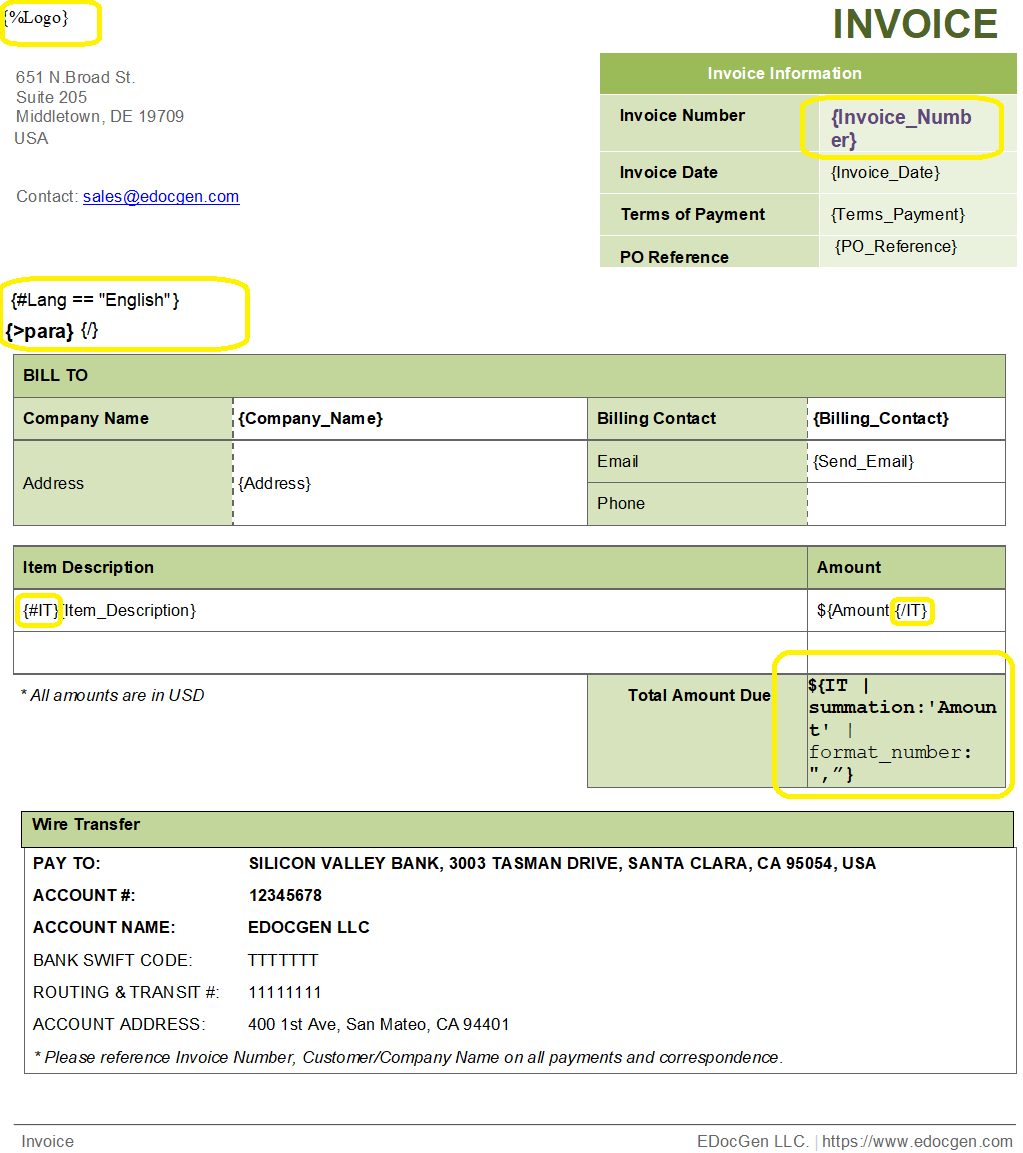
Not just that, these tags also allow the server to dynamically insert various types of content such as text, images, tables directly into your documents.
This flexibility makes it easy to create fully customized, professional documents tailored to your data.
Note - This is a one-time setup, so once the template is ready, it can be reused to generate documents in bulk.
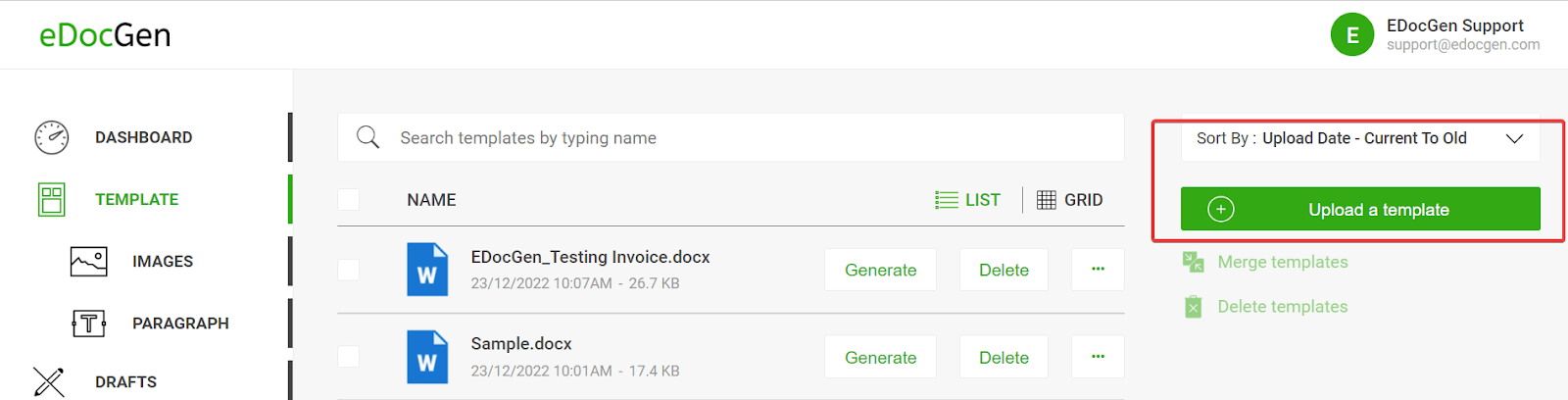
Once your template is ready, upload it to the EDocGen server.
This can be done in two ways:
API Details:
|
Method |
Endpoint |
Description |
|
POST |
/api/v1/document |
Upload template to the system server |
|
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|
documentFile |
file |
(formData) File to upload as a template |
Uploading the template ensures it’s ready for document generation, and it can be easily accessed for future tasks.
After uploading your template to the EDocGen server, the next step is to retrieve the Template ID, which is required for generating documents.
API Details:
|
Method |
Endpoint |
Description |
|
GET |
/api/v1/document/{filename} |
Returns all template details for the specified filename |
|
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|
filename |
path |
Filename of the uploaded template (e.g., edocgen.docx) |
To achieve this, use the following Python code:
```
@classmethod
def getTemplateIdviaFileName(self, filename):
base_url = "https://app.edocgen.com"
#Generate request
url = "%s/api/v1/document/?search_column=filename&search_value=%s" % (base_url, filename)
headers = {
'x-access-token': eDocGenapi.token
}
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
output = response.json()["documents"]
#print (output)
print('Template Ids are as follow for given filename')
for d in output:
print(d['_id'])
```
This function fetches the Template ID by making a GET request to the EDocGen API using the filename.
With the Template ID ready, you can now generate documents using data files in formats like JSON, XLSX, or XML.
|
Method |
Endpoint |
|
POST |
/api/v1/document/generate/bulk |
|
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|
documentId |
Form Data |
ID of the uploaded template |
|
format |
Form Data |
Output format (pdf or docx) supported by the template |
|
outputFileName |
Form Data |
Name for the generated output file |
|
inputFile |
Form Data |
Data file in JSON, XLSX, or XML format |
By using the /api/v1/document/generate/bulk endpoint, you can quickly and easily generate many documents with a single API call, saving time and hassle.
This API supports two modes of generation:
Perform this easily by using the code below:
```
@classmethod
def downloadBulkJson(self):
inputFile = "JSON_Data.json"
generated_format = "pdf"
documentId = "62f063426844520f75344091"
format = "pdf"
keyToFileName = "prefix"
base_url = "https://app.edocgen.com"
with open(inputFile, 'r') as f:
data = json.load(f)
#print(data)
#print(len(data))
if ( len(data) > 1):
generated_format = "zip"
#Generate request
url = "%s/api/v1/document/generate/bulk" % base_url
# the output file extension will be added automatically by the system
outputFileName = "%s" %uuid.uuid4()
inputValues = {
'documentId': (None, documentId),
'format': (None, format),
'outputFileName': (None, outputFileName),
'keyToFileName': (None, keyToFileName),
'inputFile': (os.path.basename(inputFile), open(inputFile, 'rb'), 'application/octet-stream')
}
headers = {
'x-access-token': eDocGenapi.token
}
response = requests.post(url, files=inputValues, headers=headers)
print("Generate document: %s" % response.json())
# add extension again due to internal bug
outName = "%s.%s" % (response.json()['outFile'], generated_format)
#Wait for file to get generated and download
url = "%s/api/v1/output/name/%s" %(base_url, outName)
print("Fetching files with name using url: %s" %url)
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
output = response.json()["output"][0] if "output" in response.json() and len(response.json()["output"]) > 0 else None
generated_file_id = None
while(not output):
print("waiting for file to get generated...", outName)
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
output = response.json()["output"][0] if "output" in response.json() and len(response.json()["output"]) > 0 else None
generated_file_id = output["_id"]
print("generated file id: %s" % generated_file_id)
# Download the generated file
url = '%s/api/v1/output/download/%s' %(base_url, generated_file_id)
download_to_file = "./%s.%s" % (generated_file_id,generated_format )
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers, allow_redirects=True)
print("file saved via name : %s" % download_to_file)
open(download_to_file, 'wb').write(response.content)
```
Explaining the code:
Here, we created a method called downloadBulkJson, which generates and downloads the documents.
This method automates the entire document generation and download process, handling both small and large-scale outputs efficiently.
EDocGen also provides the flexibility to generate documents directly from records stored in databases such as SQL tables, MongoDB collections, and more.
This is particularly useful for businesses handling large datasets and needing automated document generation at scale.
The API for generating documents from databases works similarly to document generation using JSON. However, it requires additional metadata such as database connection details, the number of records to fetch, and the table name.
API Details:
|
Method |
Endpoint |
|
POST |
/api/v1/document/generate/bulk |
|
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|
documentId |
string |
(formData) id of the template |
|
dbVendor |
string |
(formData) Database vendor |
|
dbUrl |
string |
(formData) Database connection url |
|
dbPassword |
string |
(formData) Database password |
|
dbQuery |
string |
(formData) Database select query |
|
dbLimit |
string |
(formData) Database limit number of rows from select query |
|
format |
string |
(formData) output format docx or pdf. Default docx |
|
outputFileName |
string |
(formData) file name for the output file |
Once this is done, EDocGen takes care of generating the documents automatically.
Python Code:
```
@classmethod
def downloadBulkDB(self):
format = "pdf"
dbVendor = "mysql"
dbUrl ="jdbc:mysql://sql6511576@sql6.freesqldatabase.com:3306/sql6511576/sdtest"
dbPassword = "thepassword"
dbQuery = "select * from sdtest"
dbLimit = "100"
documentId = "62f063426844520f75344091"
keyToFileName = "prefix"
generated_format = "zip"
base_url = "https://app.edocgen.com"
#Generate request
url = "%s/api/v1/document/generate/bulk" % base_url
# the output file extension will be added automatically by the EDocGen system
outputFileName = "%s" %uuid.uuid4()
inputValues = {
'documentId': (None, documentId),
'format': (None, format),
'outputFileName': (None, outputFileName),
'dbVendor': (None, dbVendor),
'dbUrl': (None, dbUrl),
'dbPassword': (None, dbPassword),
'dbQuery': (None, dbQuery),
'dbLimit': (None, dbLimit),
'keyToFileName': (None, keyToFileName),
}
headers = {
'x-access-token': eDocGenapi.token
}
response = requests.post(url, files=inputValues, headers=headers)
print("Generate document: %s" % response.json())
# add extension again due to internal bug
outName = "%s.%s" % (response.json()['outFile'], generated_format)
#Wait for file to get generated and download
url = "%s/api/v1/output/name/%s" %(base_url, outName)
print("Fetching files with name using url: %s" %url)
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
output = response.json()["output"][0] if "output" in response.json() and len(response.json()["output"]) > 0 else None
generated_file_id = None
while(not output):
print("waiting for file to get generated...", outName)
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
output = response.json()["output"][0] if "output" in response.json() and len(response.json()["output"]) > 0 else None
generated_file_id = output["_id"]
print("generated file id: %s" % generated_file_id)
# Download the generated file
url = '%s/api/v1/output/download/%s' %(base_url, generated_file_id)
download_to_file = "./%s.%s" % (generated_file_id,generated_format )
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers, allow_redirects=True)
print("file saved via name : %s" % download_to_file)
open(download_to_file, 'wb').write(response.content)
```
Explaining of the Code:
Now that your documents are ready, it’s time to put them to work. Let’s look at how EDocGen makes it easy to manage and share your documents.
Once your document is ready, you can send it directly to any recipient, without the need to download or manually attach files. This is powered by eDocGen's built-in email functionality, making document sharing quick and effortless.
All it takes is the document’s Output ID and the recipient’s email address.
Use this code:
```
@classmethod
def sendOutputToEmail(self , outputId,emailId):
base_url = "https://app.edocgen.com"
#Generate request
url = "%s/api/v1/output/email" % base_url
headers = {
'x-access-token': eDocGenapi.token
}
inputValues = {
'outId': (None, outputId),
'emailId': (None, emailId),
}
response = requests.post(url, files=inputValues, headers=headers)
output = response.json()
print (output)
```
Why This Helps:
This feature is perfect for teams that need to share documents quickly and consistently, saving time and effort.
If you prefer to download your documents, eDocGen makes it just as easy.
Depending on how many documents you generate, you’ll get either a single file (PDF/DOCX) or a compressed .zip file for bulk downloads.
This way, your files are always organized and ready to use, whether you're archiving them or sharing them manually.
Pro Tip: Before sharing your documents, double-check that your templates are properly formatted and your API tokens are up to date.
Once your documents are shared or downloaded, your workflow is almost complete.
However, a few smart checks can make the process even smoother. So, it’s worth pausing to think about a few key takeaways that can help you avoid common pitfalls.
Let’s review them next!
While automating document generation with Python and eDocGen is designed to be simple, paying attention to small details can save you time and prevent avoidable issues.For a smoother, more secure experience, here are a few best practices to help you get the most out of the process:
By now, you’ve seen how effortless document generation can be with eDocGen, it being a truly compelling solution for automating document workflows of businesses of all sizes.
If you’re ready to start scaling your operations, Link today!